What is Keratoplasty?
Keratoplasty, medically known as corneal transplantation, is the process of changing the corneal layer of the eye. The cornea is a transparent tissue located at the front of the eye that refracts light and focuses it on the retina. The quality of vision largely depends on the cornea being healthy and regular. However, in some cases, damage, deformity or blurring may occur in the cornea. Keratoplasty is a successful treatment method for solving such problems.
İçindekiler
Toggle
Keratoplasty Types
Keratoplasty procedure is performed in different types according to the needs of the patient. These are:
Penetrating Keratoplasty (PK) It is a full-layer corneal transplant. The entire corneal layer is removed and replaced with healthy corneal tissue taken from a donor. It is especially suitable for patients with severe corneal clouding and scars.
Lamellar Keratoplasty It is a procedure in which only certain layers of the cornea are replaced. The subtypes of this method are:
DALK (Deep Anterior Lamellar Keratoplasty): The outer layers of the cornea are replaced. This method is preferred in cases where the endothelial cells in the inner part of the cornea are healthy.
DSAEK/DMEK (Descemet’s Stripping Endothelial Keratoplasty): The endothelial layer in the inner part of the cornea is replaced. It is suitable for diseases caused by endothelial cell damage.
Keratoplasty Application Areas
Keratoplasty is widely used in the treatment of the following conditions:
Keratoconus: A disease characterized by the thinning and sharpening of the cornea.
Corneal Injuries: Damage caused by trauma or chemical burns.
Fuchs Endothelial Dystrophy: Damage to corneal endothelial cells.
Corneal Infections: Infections that leave scar tissue, especially in advanced stages.
Corneal Clouding: Loss of transparency of the cornea due to genetic or acquired causes.
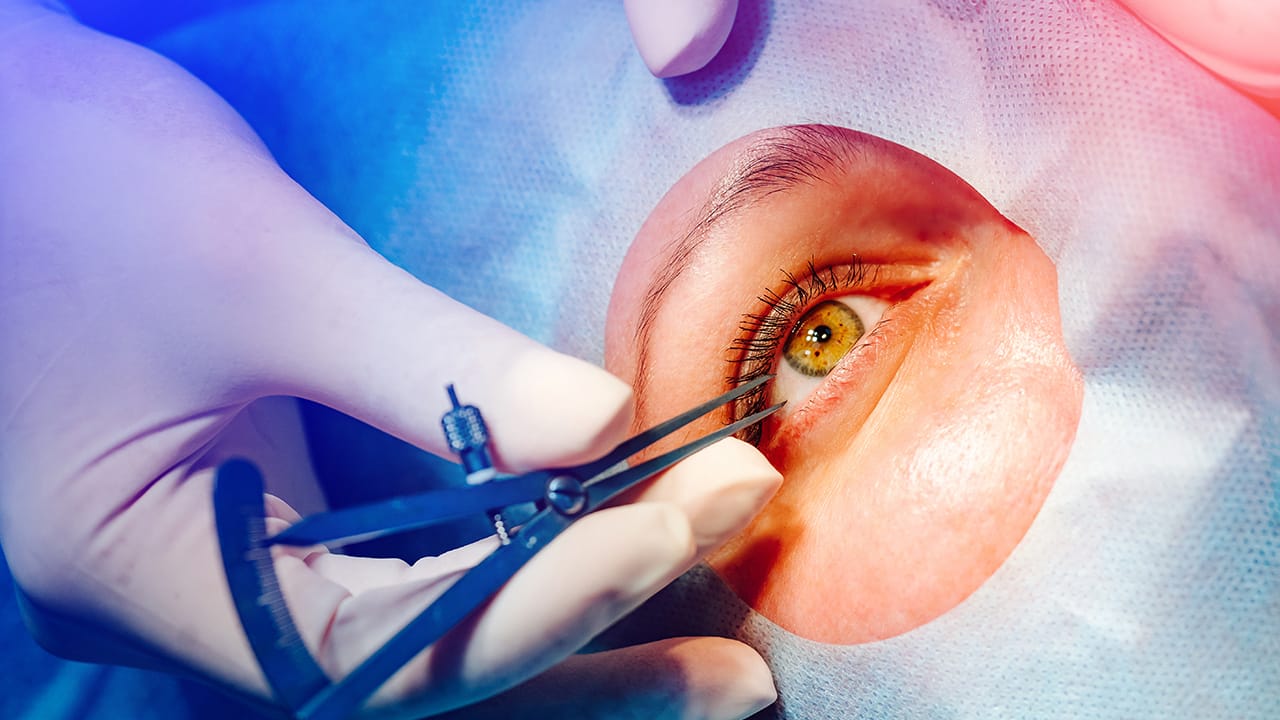
Surgery Process
Keratoplasty surgery is usually performed under local or general anesthesia. The procedure steps are as follows:
Preparation: Donor corneal tissue is obtained and tested before the procedure.
Corneal Removal: The patient’s damaged corneal area is removed with surgical instruments.
New Cornea Placement: The donor cornea is cut to the appropriate size and stitched in place.
Stitching: The corneal tissue is fixed with fine stitches. The stitches are usually removed months after the surgery.
Post-Surgery Process
The recovery process after surgery can vary from a few months to a year. The patient should go to the doctor regularly and pay attention to the following points:
Use of Eye Drops: It is important to use the prescribed drops regularly to reduce the risk of infection and inflammation.
Restriction of Physical Activity: Heavy activities that may cause pressure on the eye should be avoided.
Checks: Regular check-ups with the doctor are necessary to prevent possible complications.
Possible Complications
Keratoplasty is generally a safe procedure, but it does carry some risks. These risks include:
Transplant Rejection: The body’s rejection of the donor tissue, perceiving it as foreign.
Infection: Risk of infection after the surgical procedure.
Increased Pressure in the Eye (Glaucoma): Another complication that may occur after surgery.
Astigmatism: Visual impairment due to irregularity of the corneal surface.
Results and Success Rate
Keratoplasty is an effective treatment method that can prevent serious vision loss and improve quality of life. Thanks to modern surgical techniques and better preservation of donor tissues, the success rate is quite high. The vast majority of patients regain their vision significantly after surgery.
In conclusion, keratoplasty plays a critical role in the treatment of eye diseases. However, as with any surgical procedure, this procedure requires careful evaluation and preparation.